A good automation framework is essential for testing goals to be achieved. Better the foundation of the automation framework, automation strategy formulation and its implementation, will lead to achieving long-term ROI.
Some of the foundational characteristics of automation frameworks:
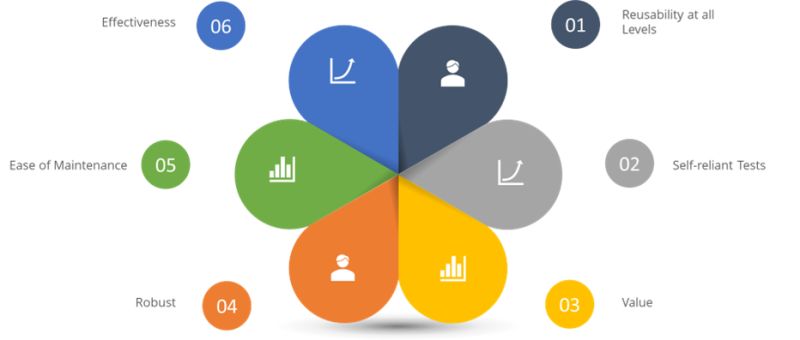
1. Reusability & Modularity
- Framework and its scripts should be flexible so that it can be leveraged on different releases, configurations & environments.
- A modular framework is one where the components of the framework are separated and can be modified or replaced independently, making the overall system more flexible and maintainable.
2. Self-reliant Tests
- Ability to run Automated test script cases in any order independently.
- The capability of running automated tests without the need for external resources or support.
- Reliable and resistant to errors.
3. Value
- Delivers measurable value in terms of wider test coverage, tests extended data conditions, decreased cycles of execution, decreased effort and improved quality.
- Enhances the reliability and robustness of the software by identifying defects early.
- Leads to better user experiences by ensuring the software meets high-quality standards.
4. Robust
- Ensure that automated tests are reliable and provide consistent and accurate results, even in the most challenging testing environments.
- Provides mechanisms to handle exceptions and errors without failing the entire test suite.
- Adapts to changes in the application with minimal modifications.
5. Ease of Maintenance
- The framework should be of low maintenance and should not take significant effort to handle routine changes to the Application Under the Test.
- Facilitates collaboration among team members by providing clear guidelines and documentation.
- Reduces the time required to update or modify the framework.
6. Effectiveness
- Effective in identifying defects of significance and adopted by Developers & Testers
- Increased confidence in the test coverage.
- Increases the likelihood of identifying and addressing defects early in the development cycle.
7. Scalable
- Framework should be scalable to an increasing number of testing scopes, a variety of tests, technological execution environment.
- Supports the expansion of the test suite as the application grows and evolves.
- Maintains performance and reliability even as the number of tests increases.